Recycling Lives Services: A Total Solution for Company Recycling
Discovering Various Types of Waste in Modern Waste Management Systems
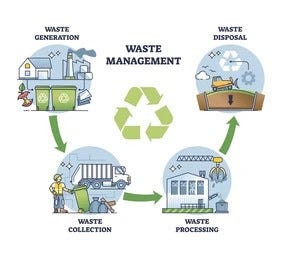
The contemporary landscape of waste management includes browsing a complex range of waste kinds, each needing specialized handling and disposal approaches to alleviate environmental influences. Local strong waste, dangerous waste, digital waste, and natural waste each existing distinct difficulties and possibilities for resource recovery. Ingenious services such as clever waste containers and waste-to-energy innovations are arising as crucial devices in boosting performance and sustainability. Recognizing these waste types is necessary for fostering public recognition and motivating active involvement in lasting methods. What techniques can efficiently resolve these diverse sorts of waste while advertising a circular economic situation?
Local Strong Waste
Local solid waste, usually referred to as family garbage or garbage, encompasses a range of disposed of materials created by residential, industrial, and institutional sources within a district. This waste stream generally includes items such as product packaging, food scraps, yard trimmings, paper, plastics, fabrics, and thrown out family products. The administration of local solid waste is a vital part of city planning and public health and wellness, requiring reliable collection, transport, and disposal systems.
Efficient waste monitoring systems are developed to lessen ecological impact while making best use of source healing. This typically entails a mix of methods including landfilling, composting, and recycling. Recycling programs target materials like paper, glass, metals, and particular plastics, diverting them from landfills and reintroducing them right into the production cycle. Composting natural waste, such as food scraps and lawn trimmings, not only minimizes garbage dump usage however likewise generates useful dirt modifications.
Communities should additionally address the financial and logistical difficulties connected with waste monitoring. Executing pay-as-you-throw systems, improving public awareness, and purchasing modern technology can significantly improve waste diversion rates. By incorporating these methods, districts can foster sustainable areas, minimize greenhouse gas discharges, and conserve all-natural resources.
Contaminated Materials

Effective harmful waste monitoring entails numerous important steps: identification, segregation, disposal, and therapy. Partition guarantees that unsafe materials are saved individually from non-hazardous waste to prevent cross-contamination.
Governing frameworks, such as the Resource Preservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States, provide standards and criteria for harmful waste administration. Adherence to these guidelines, combined with innovations in waste treatment modern technologies, is important in mitigating the threats related to contaminated materials.
Digital Waste
Electronic waste, generally described as e-waste, represents a swiftly growing challenge in waste management systems worldwide. This sort of waste incorporates thrown out digital devices and devices such as mobile phones, computers, televisions, and other digital home appliances. The rapid speed of technical improvement, paired with lowering product lifespans and consumer demand for the most up to date tools, has actually exponentially raised the volume of e-waste produced annually.
E-waste is specifically bothersome as a result of its intricate structure, usually having unsafe substances like lead, cadmium, and mercury, which posture substantial environmental and wellness risks if not appropriately managed. Alternatively, e-waste also contains useful products such as gold, copper, and silver, which can be recovered and recycled. The twin nature of e-waste-- both important and unsafe-- necessitates specialized handling, reusing, and disposal processes.
Reliable e-waste monitoring involves rigorous governing frameworks, durable collection systems, and navigate to this site advanced reusing innovations. Public understanding and engagement are essential, as incorrect disposal practices, such as prohibited unloading and informal recycling, exacerbate ecological contamination and carcinogen. As a result, enhancing e-waste administration methods is vital for alleviating environmental effect and recovering beneficial sources in an increasingly digital world.
Organic Waste
Organic waste, comprising cooking area scraps, backyard trimmings, and agricultural deposits, represents a substantial section of the worldwide waste stream. This type of waste is biodegradable, suggesting it can be broken down by microbes into easier organic compounds. Regardless of its possibility for natural decay, improper administration of natural waste can lead to negative ecological effects, including the discharge of greenhouse gases such as methane, which add to climate change.
Effective monitoring of natural waste is essential for decreasing these environmental influences (recycling lives services). Composting is an extensively adopted technique, changing natural waste into nutrient-rich compost that can improve dirt wellness and farming productivity. Additionally, anaerobic digestion is an arising innovation that converts organic waste into biogas, a sustainable energy resource, and digestate, which can be made use of as plant food
Municipalities and waste management entities have to apply durable organic waste collection and therapy programs to optimize the benefits of these procedures. Public education projects can likewise play a critical duty in motivating families and companies to separate organic waste from various other kinds of waste. By prioritizing the administration of natural waste, societies can minimize land fill usage, reduced greenhouse gas exhausts, and create valuable byproducts for agricultural use.

Ingenious Waste Monitoring
In the realm of waste monitoring, ingenious approaches are transforming just how societies manage their refuse, intending for sustainability and performance. One popular innovation is the application of clever waste containers outfitted with sensing units that keep track of fill levels and enhance collection paths.
Another significant development is the adoption of waste-to-energy (WtE) technologies. By transforming non-recyclable waste into useful energy through procedures such as incineration and anaerobic digestion, WtE lowers garbage dump worry and offers a renewable energy resource. Additionally, innovations in chemical recycling permit the failure of complex plastics into their initial monomers, making it possible for the production of new, high-quality plastic products.
Additionally, the round economic climate version is acquiring grip, highlighting the layout of products and systems that prioritize reusability and resource performance. This holistic approach encourages sectors to lessen waste generation from the beginning. With these cutting-edge techniques, modern waste monitoring systems are not just attending to the immediate obstacles of garbage disposal however additionally leading the way for an extra sustainable future.
Final Thought
A detailed understanding of local strong waste, hazardous waste, digital waste, and organic waste, combined with the implementation of cutting-edge waste management remedies, is imperative for minimizing ecological influences. Incorporating modern technologies such as clever waste bins and waste-to-energy systems can boost performance and sustainability. Efficient waste site here administration methods not just foster source recovery but likewise advertise public understanding and involvement, ultimately adding to the advancement of a circular economy.
The modern landscape of waste monitoring involves navigating a complicated variety of waste kinds, each needing specialized handling and disposal techniques to alleviate ecological impacts. Community solid waste, harmful read this waste, electronic waste, and organic waste each existing unique difficulties and opportunities for source healing.Electronic waste, typically referred to as e-waste, represents a rapidly expanding challenge in waste administration systems around the world. Through these cutting-edge approaches, modern-day waste monitoring systems are not just dealing with the prompt challenges of waste disposal yet likewise paving the means for an extra sustainable future.
A thorough understanding of metropolitan solid waste, hazardous waste, electronic waste, and natural waste, combined with the application of ingenious waste monitoring options, is crucial for reducing ecological impacts. (recycling lives services)